In this series, master woodworker Brent Hull will introduce readers to the different architectural styles that were popularized throughout American history, explaining their significance and unique design features.
No architectural style has captured the imagination of an American era like Greek Revival. Lasting from 1820 to 1860, it was more than just a style; it was an ideal that expressed itself in the architecture of our young nation and as an ideological assurance that the democracy could and would survive. We forget that 200 years ago, the concept of a democratic rule, by the people and for the people, was a radical model and still an experiment. The American Revolution, and our breaking from European molds of government, was itself revolutionary. The popularity of the Greek Revival style coincided with the rise of America into a nation. This is a style that projects permanence and strength, traits our young country desired.

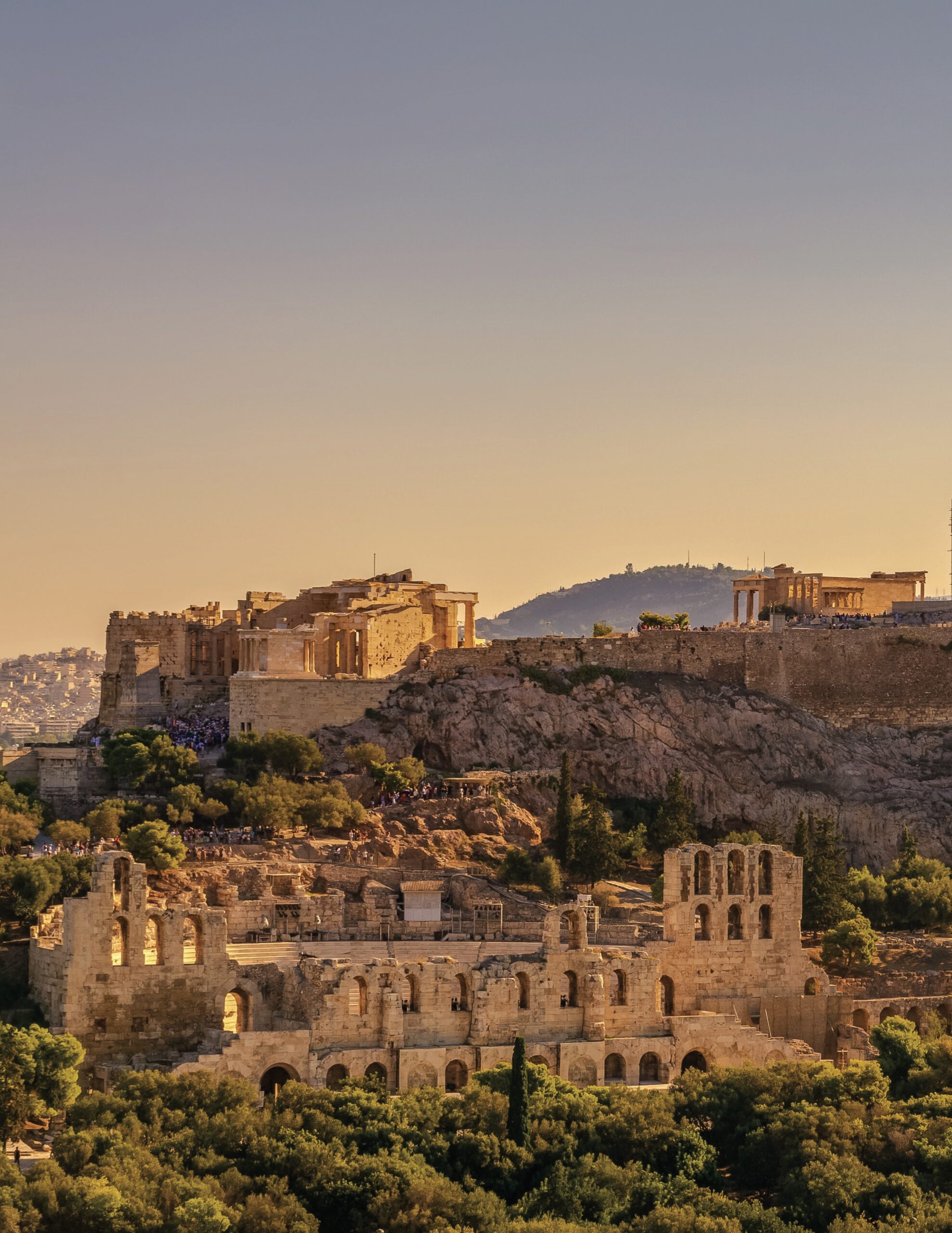
The Greek Revival style is most identifiable by its temple front, which is inspired by the Parthenon in Greece. This famous temple sits on the Acropolis in Athens—the tall rock formation that stands proudly over the city and was a place of worship to Athena, patron goddess of Athens. The Parthenon has been studied and revered for centuries because of its mathematical purity and design integrity. Though the Greek Revival era in America lasted from 1820 to 1860, the interest in Greek culture had been developing for some time in Europe. By 1750 in England, the ancient Roman world had been studied and extensively explored. It had been almost two centuries since Andrea Palladio, 16th-century Italian architect, wrote “I quattro libri dell’architettura” (“The Four Books of Architecture”) in 1570. This book was on the shelves of many prominent builders and architects and became the blueprint for design and construction based upon the classical characteristics.
Interestingly, Palladio had only ever studied ancient Rome. By 1750, it was well known that Greece had been the key influence on Roman architecture. The Romans had appropriated and adopted the ideas that the Greeks had perfected. Greece and ancient Greek culture were hidden and veiled by the Ottoman Turkish Empire (mid 15th century to early 19th century), which refused to let travelers into the country for fear of spying.
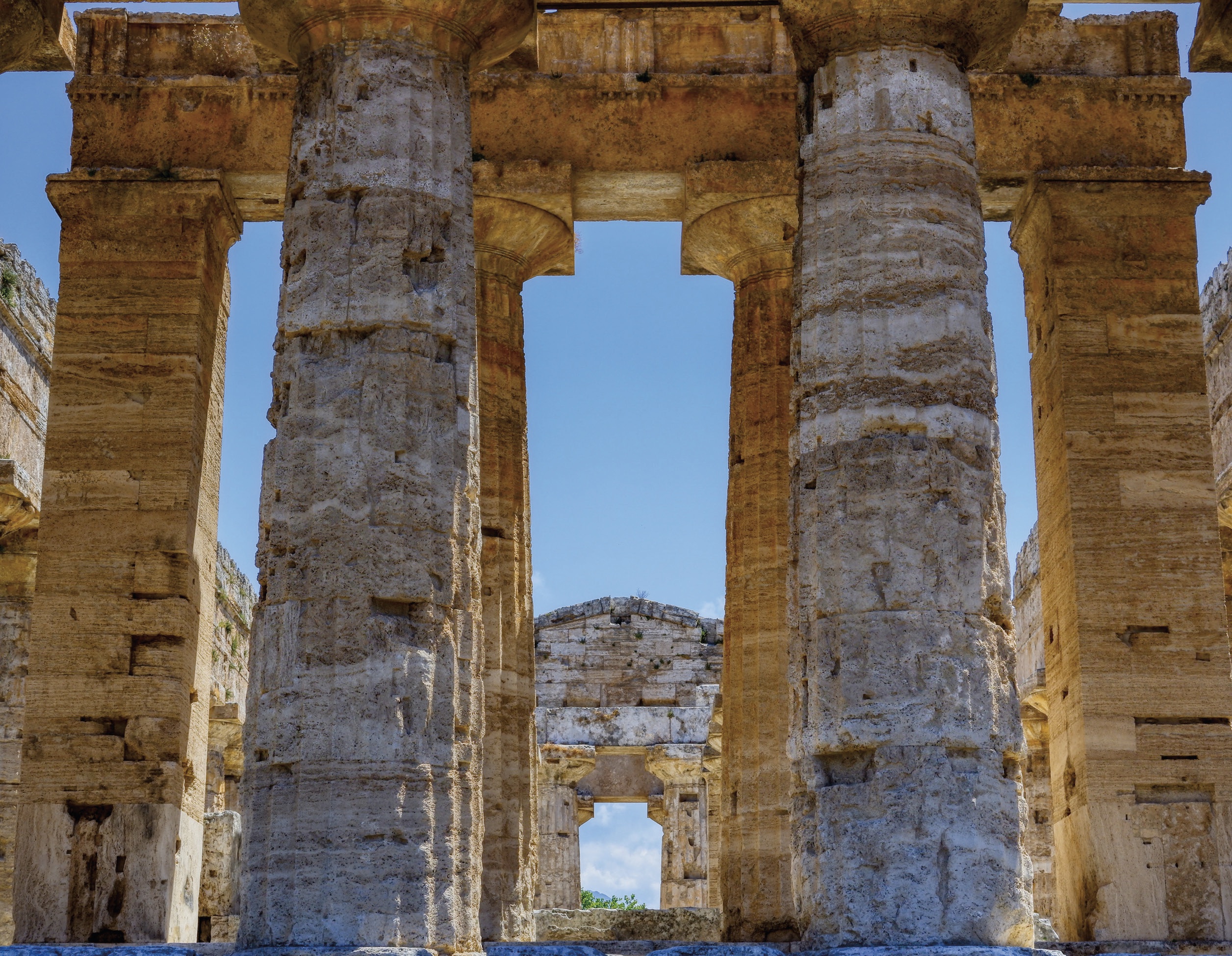

Travel to Greece in the 18th century was dangerous; thus, a secret mission was hatched by a spirited group of thinkers. Two Englishmen by the names of James Stuart (archaeologist, architect, and artist) and Nicholas Revett (architect) traveled to Athens in 1751, funded and organized by the Society of Dilettanti of London. Disguised as native Turks, they secretly drew and chronicled the ancient Greek ruins, making accurate measurements of the Acropolis of Athens and the Parthenon. This mission resulted in the seminal book, “The Antiquities of Athens,” which was written in three volumes over a 40-year period. After these discoveries were published in 1758, the work became a source book on ancient Greek architecture.
“The Antiquities of Athens” spurred great interest and encouraged architects to build in new forms and with fresh inspiration. The book highlighted how Greek designs were different from Roman temples and buildings. For instance, Greek architects did not use arches in their designs; the arch was a Roman improvement. Greek temples like the Parthenon were beautiful and admired for their near-mathematical perfection and symmetry. The proportions of the Parthenon match the proportions of the human body; the columns to beams have a proportional relationship much like the human form, where head to hand are proportional.
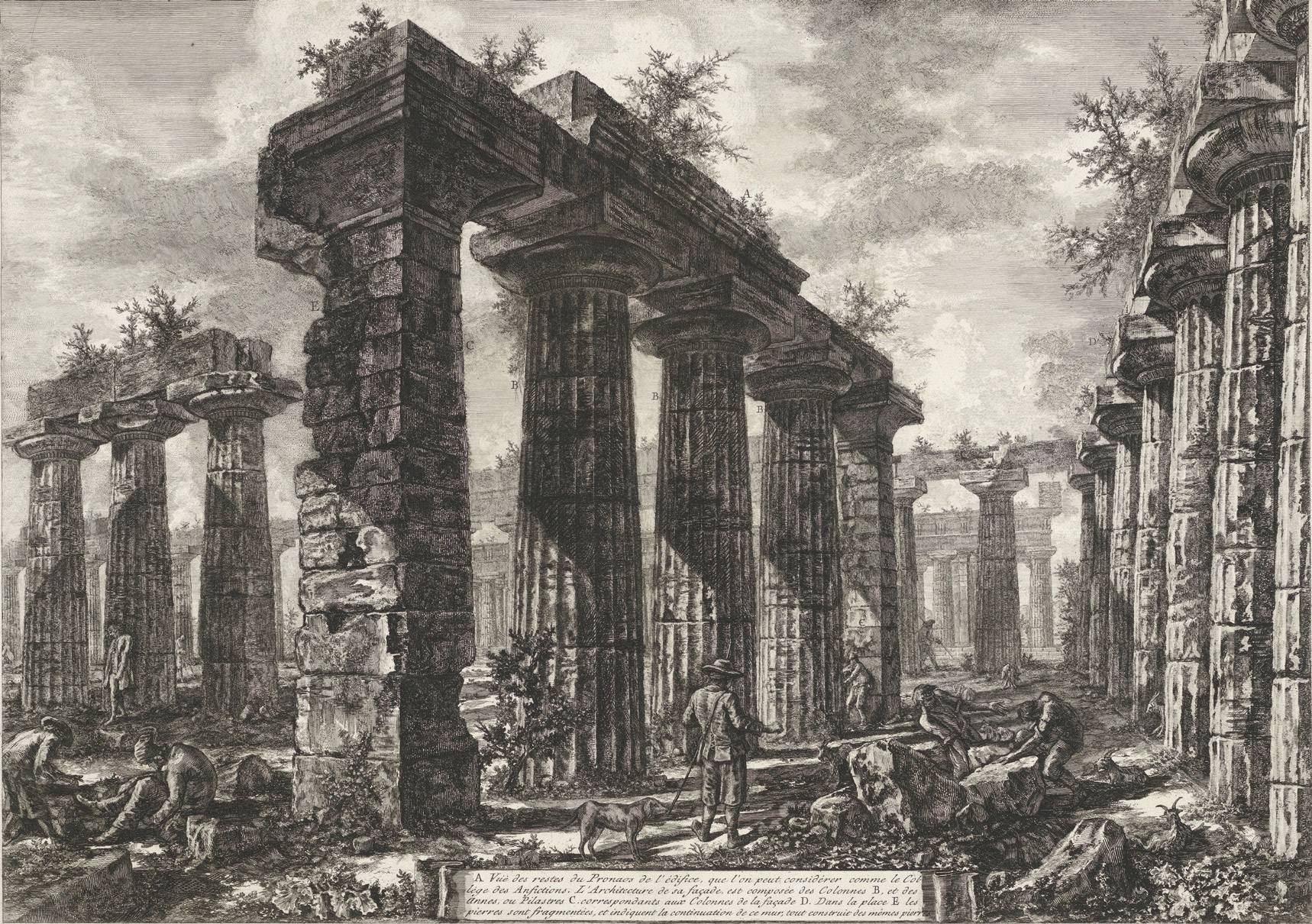


The interest in Greek culture continued to grow through the late 18th and early 19th centuries. The rediscovery of the Greek temples at Paestum (550 to 450 B.C.) in southern Italy, during the 18th century, was a marvel. The presence of the three well-preserved Greek temples, in the region of Italy (present day Calabria), reinforced the idea of original Greek dominance of the world under Alexander (356–323 B.C.). This temple was made more popular in 1778 after the well-known engraver Giovanni Battista Piranesi drew the temple and prints became readily accessible to the public.
Americans’ interest in the Greek Revival style benefited from the War of 1812 between Britain and America. These battles soured the nation’s interest in British design and culture. Naturally looking for inspiration from more remote places, the story of Greece as an original democracy was contagious. In the early 1820s, the war for Greek independence from the Ottoman Turkish Empire began, and it reminded Americans of their fight for independence. The Greek war for independence was front-page news, and it became more compelling as Lord Byron, the famous English poet, died in 1824 from a fever contracted while training Greek troops after the First and Second Siege of Missolonghi.
How much did all this excite the imagination of the American people? Maybe we need to look no further than the naming of many of our towns and cities from this period. Athens, Georgia, the college town famous for the Georgia Bulldogs, was given the name Athens in honor of Plato and Aristotle’s school of thought. The actual number of towns named after Greek cities and citizens is profound. Consider these names: Sparta, Athens, Ithaca, Syracuse, Alexandria, Akron, and Atlanta, from the Greek god Atlas. It is clear Greek culture and thinking inspired not just architecture but how Americans thought of themselves as a people.
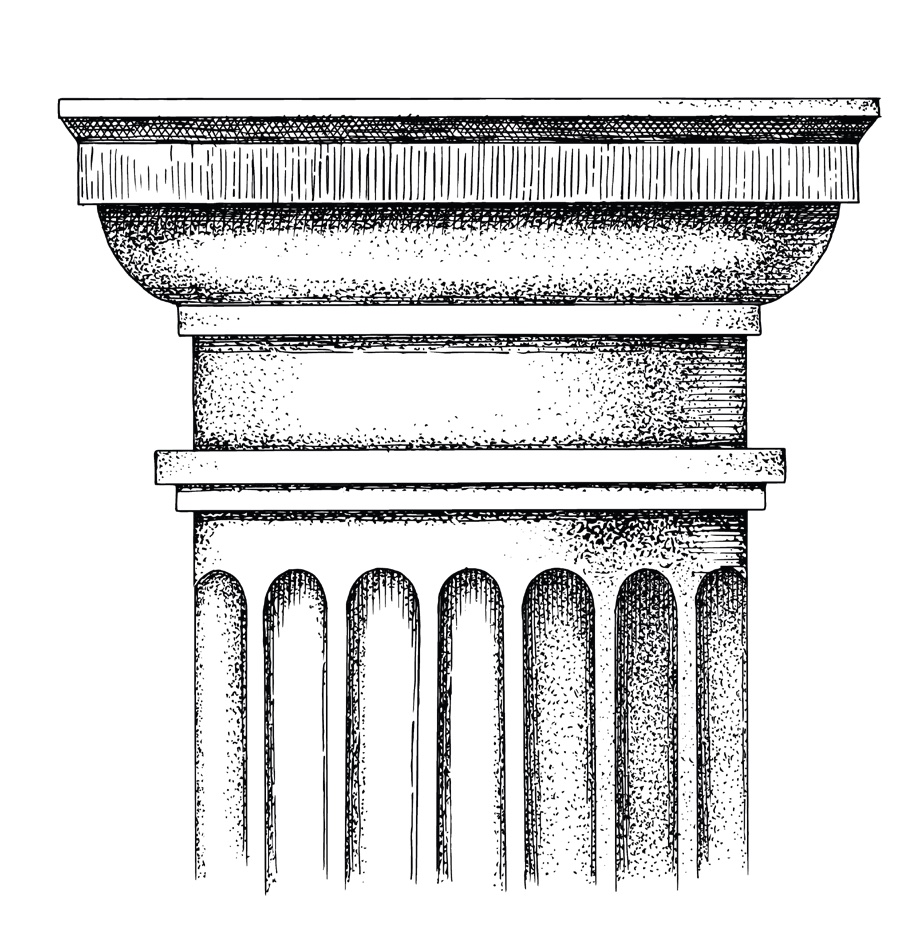
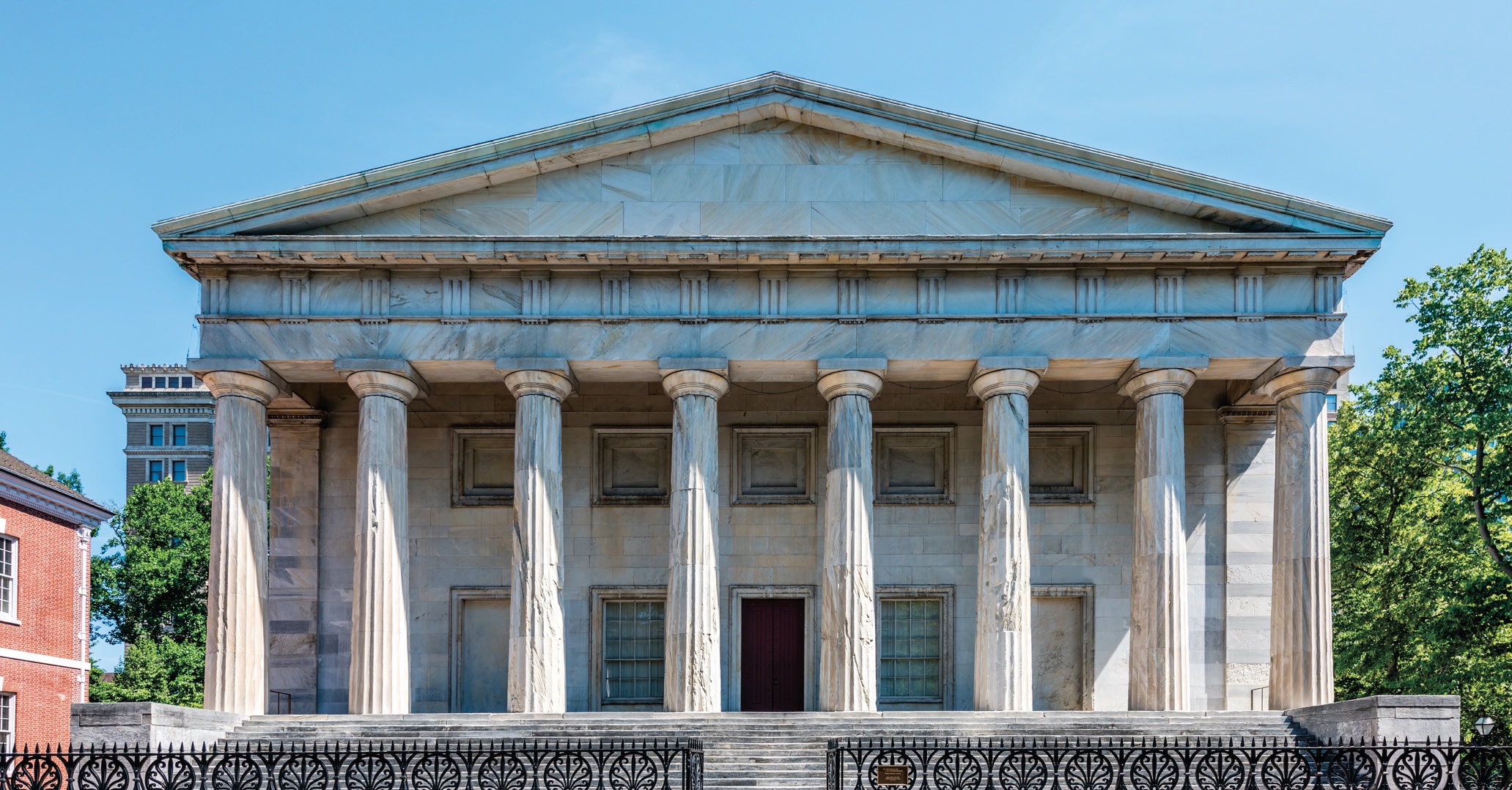
Greek Revival architecture today is readily identifiable by several key attributes: a temple front, large Doric columns with no bases, and simple and bold stone-like ornamentation with a triangular pediment. The Second Bank of the United States, Philadelphia, is a wonderful example of the Greek Revival style. Now part of Independence Park in Philadelphia, the bank was built between 1818 and 1824 by William Strickland, noted Philadelphia architect and civil engineer. With strong fluted Doric columns that sit directly on the raised stylobate (raised platform), the Second Bank of the United States was clearly inspired by the Parthenon in Greece. The bank’s eight columns have no base, which is a unique style of ancient Greek detail. The building’s presence is commanding and bold in character with its wide, thick columns crowned by the signature Greek triangular pediment and simple ornaments and moldings around doors and windows.
Strickland was a former student of Benjamin Latrobe, the man who is regarded as the first professionally trained American architect. Both Latrobe and Strickland were disciples of the Greek Revival style and were credited with having helped establish the Greek Revival movement in America. Some of Strickland’s most accomplished building designs were in this style. During the 19th century, the Greek Revival style extended itself into the construction of newer small towns, banks, courthouses, and other civic buildings looking to establish an air of permanence and significance.
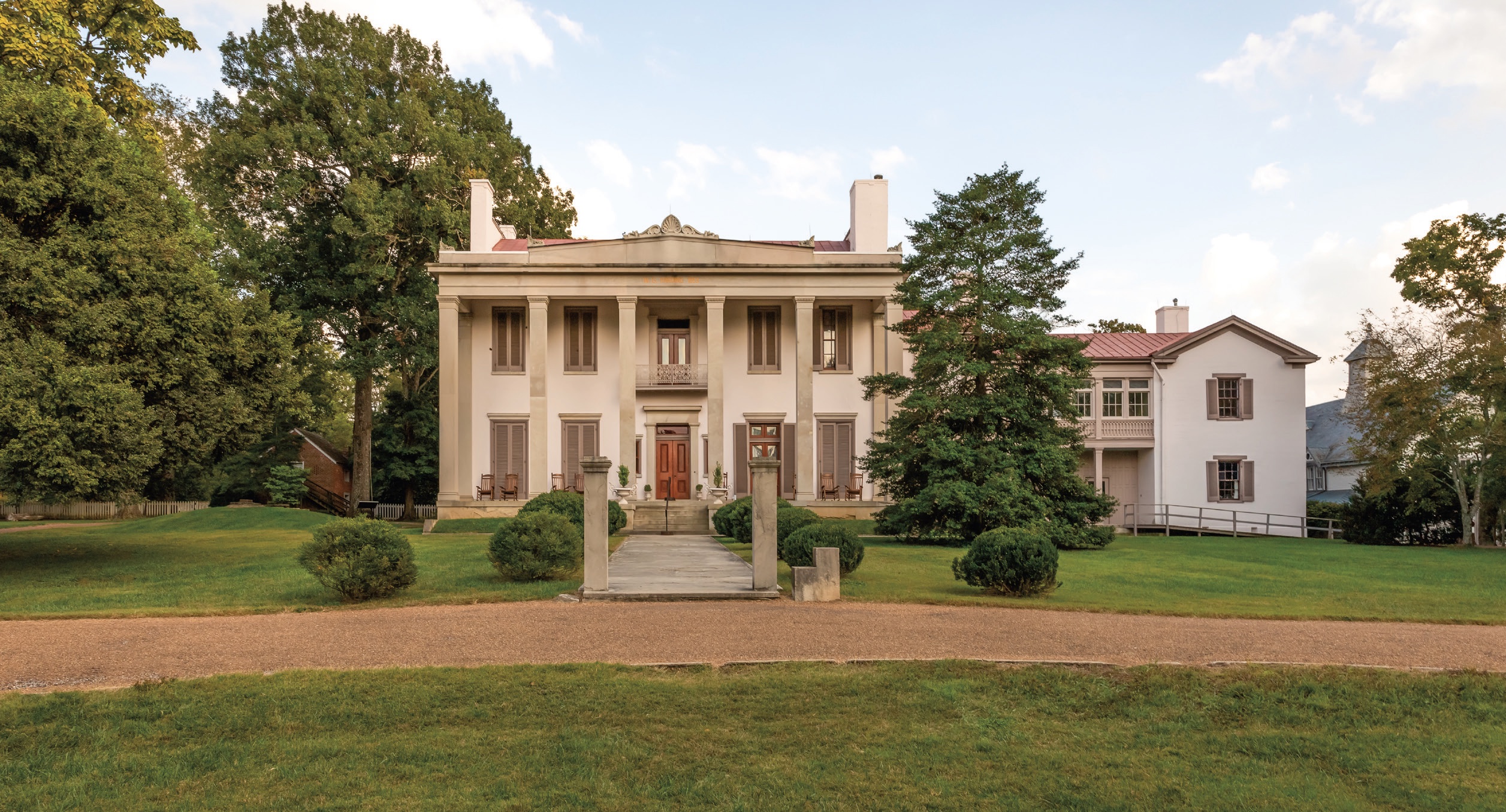


Another prominent Strickland design was the Belle Meade plantation in Nashville, Tennessee. Formerly, the two-story plantation was built in the Federal style, but after William Giles Harding took over operations at Belle Meade in 1839, he employed Strickland to construct a two-story, 24-by-55-foot addition to the home. In keeping with the Greek Revival style, the new home was “bold in silhouette, broad in proportions, and simplified in detail,” with its six limestone, Doric pillars supporting the front porch and pedimented attic.
The Greek Revival era ended when the Civil War began in the 1860s. After the war, this style was forgotten and replaced by the decorative frills of the industrialized Victorian architecture. The style is still revered today for its simple, honest character and charm. These historic buildings with strong stoic porches still remind us of a simpler time when America, as a young nation, hoped to grow and prosper.
This article was originally published in American Essence magazine.













